5.2.0 Change Notes
- [5.2.0 Change Notes](#5.2.0 Change Notes)
@itwin/core-ecschema-metadata
Additions
- Added FormatSetFormatsProvider class that implements MutableFormatsProvider to manage format definitions within a format set. This provider supports adding and removing formats at runtime and automatically updates the underlying format set when changes are made.
Changes
- Added
unitSystemproperty to FormatSet interface, using UnitSystemKey type. This will help move APIs away from relying onactiveUnitSysteminquantityFormatter, as they move to the new formatting APIs usingIModelApp.formatsProvider. Looking ahead, tools and components that use formatting APIs can then listen to just theonFormatsChangedevent fromIModelApp.formatsProviderinstead ofIModelApp.quantityFormatter.onActiveUnitSystemChanged. - Added optional
descriptionproperty to FormatSet interface. This property allows for additional descriptive text to be associated with a format set, providing better documentation and user context for format set purposes. - Changed interface for formats in
FormatSetfrom SchemaItemFormatProps to FormatDefinition. FormatSet just uses thename,label,descriptionfield fromSchemaItemFormatProps, whichFormatDefinitionalready has.
Presentation
Deprecation of hierarchy-related APIs
All hierarchies-related APIs have been deprecated in favor of the new-generation hierarchy building APIs, provided with the @itwin/presentation-hierarchies package. See the learning section and migration guide for details on how to create similar hierarchies using those APIs. See the API deprecations section for a list of specific APIs that have been deprecated.
API deprecations
@itwin/presentation-common
Deprecated all hierarchy-related types (see Deprecation of hierarchy-related APIs section for more details).
- Presentation rule types:
ChildNodeRuleChildNodeSpecificationChildNodeSpecificationBaseChildNodeSpecificationTypesClassGroupCustomNodeSpecificationCustomQueryInstanceNodesSpecificationDefaultGroupingPropertiesContainerECPropertyValueQuerySpecificationGroupingRuleGroupingSpecificationGroupingSpecificationBaseGroupingSpecificationTypesInstanceNodesOfSpecificClassesSpecificationNavigationRuleNavigationRuleBaseNodeArtifactsRulePropertyGroupPropertyRangeGroupSpecificationQuerySpecificationQuerySpecificationBaseQuerySpecificationTypesRelatedInstanceNodesSpecificationRootNodeRuleSameLabelInstanceGroupSameLabelInstanceGroupApplicationStageStringQuerySpecificationSubCondition
- Node key types:
BaseNodeKeyECClassGroupingNodeKeyECInstancesNodeKeyECPropertyGroupingNodeKeyGroupingNodeKeyLabelGroupingNodeKeyNodeKeyNodeKeyPathKeySet.nodeKeys,KeySet.nodeKeysCount,KeySetJSON.nodeKeys
- Node types:
NodeNodePathElementNodePathFilteringDataPartialNodeStandardNodeTypes
- Presentation manager prop and return types:
FilterByInstancePathsHierarchyRequestOptionsFilterByInstancePathsHierarchyRpcRequestOptionsFilterByTextHierarchyRequestOptionsFilterByTextHierarchyRpcRequestOptionsHierarchyCompareInfoHierarchyCompareOptionsHierarchyLevelHierarchyLevelDescriptorRequestOptionsHierarchyLevelDescriptorRpcRequestOptionsHierarchyRequestOptionsHierarchyRpcRequestOptionsHierarchyUpdateInfoNodeDeletionInfoNodeInsertionInfoNodeUpdateInfoPartialHierarchyModification
@itwin/presentation-backend
Deprecated all hierarchy-related types (see Deprecation of hierarchy-related APIs section for more details).
- Hierarchy cache configuration:
DiskHierarchyCacheConfigHierarchyCacheConfigHierarchyCacheModeHybridCacheConfigMemoryHierarchyCacheConfigPresentationManagerCachingConfig.hierarchies
PresentationManagermethods:PresentationManager.compareHierarchiesPresentationManager.getFilteredNodePathsPresentationManager.getNodePathsPresentationManager.getNodesPresentationManager.getNodesCountPresentationManager.getNodesDescriptor
@itwin/presentation-frontend
Deprecated all hierarchy-related types (see Deprecation of hierarchy-related APIs section for more details).
GetNodesRequestOptionsIModelHierarchyChangeEventArgsPresentationManagermethods & members:PresentationManager.getFilteredNodePathsPresentationManager.getNodePathsPresentationManager.getNodesCountPresentationManager.getNodesDescriptorPresentationManager.getNodesIteratorPresentationManager.onIModelHierarchyChanged
Display
Draco decoding
Draco decoding in iTwin.js has been changed so that the loaders.gl dependency will no longer use a CDN to request the draco-decoder source files. Instead, we now bundle those resources into iTwin.js from a new draco3d dependency. We ask the loaders.gl library to locally use those resources.
Geometry
Clippers for a curve chain
Added a new API ClipUtilities.createClippersForRegionsClosestToCurvePrimitivesXY to the clip utilities class to create clippers for regions closest to the children of a curve chain.
The API takes a curve chain (z-coordinate is ignored) and other optional inputs (which control the accuracy and xy-range of the returned clippers) and returns an ordered array of clippers, each of which represents the region closest to the corresponding primitive in the input curve chain.
Examples
A custom path is generated and passed along with control options to the API:
Below you can see the visualization of clippers. Each child is shown by a color and the corresponding region to that child is shown by a similar color. Note that regions crossed the curve chain exactly at the joins.
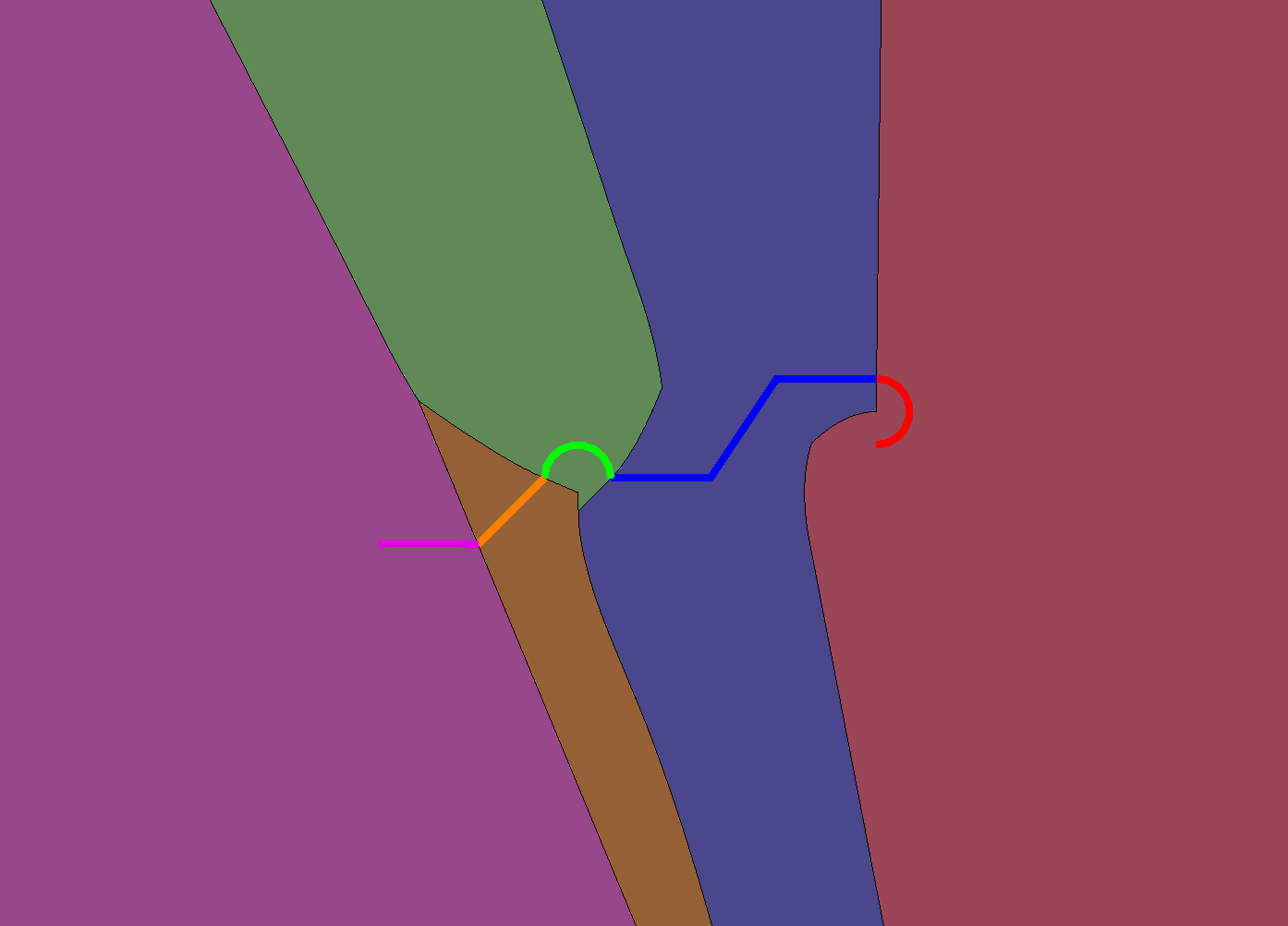
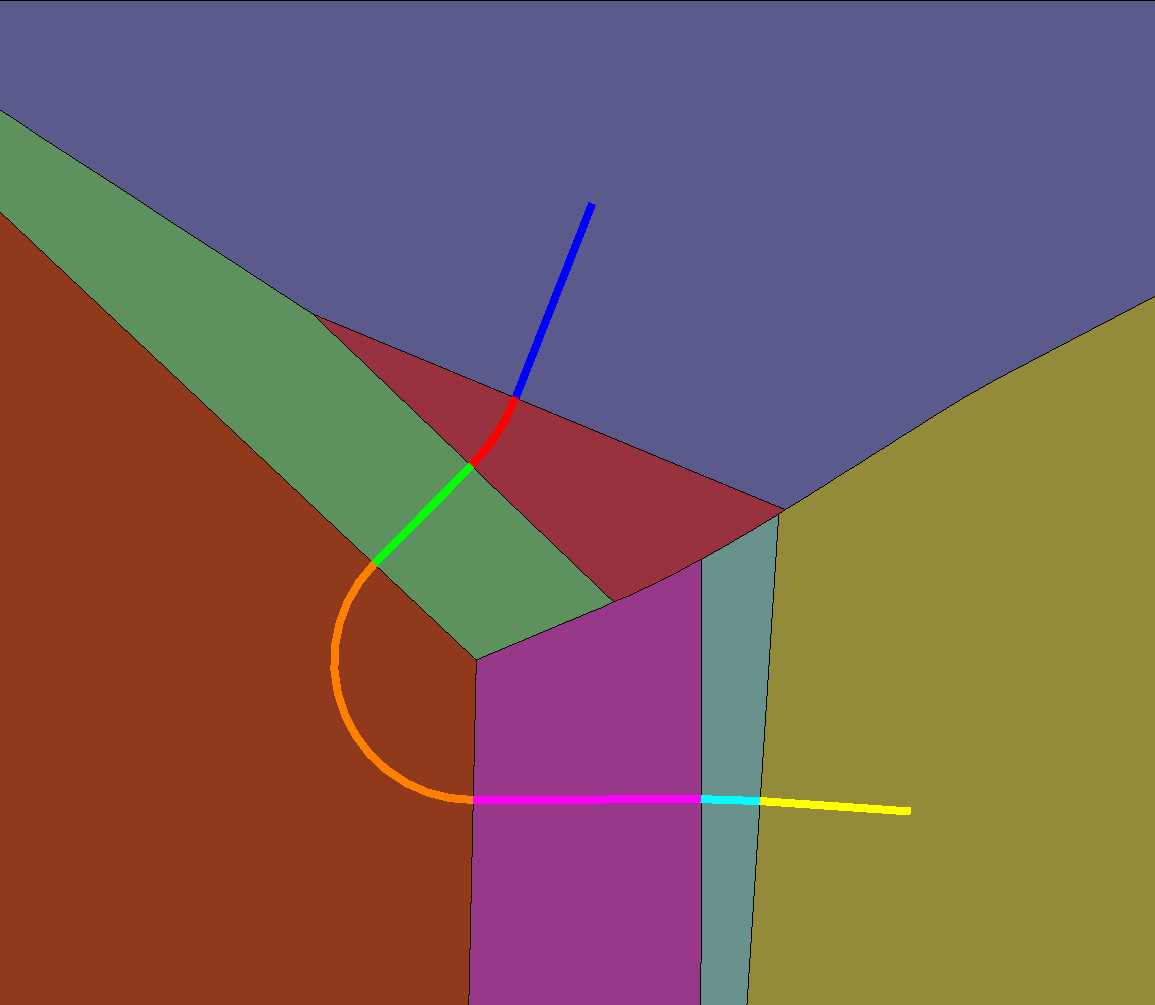
Here is another example for a path provided by the Civil team:
Electron 38 support
In addition to already supported Electron versions, iTwin.js now supports Electron 38.
Last Updated: 01 October, 2025